A Most Vexing Micro-Hydrodynamics Problem
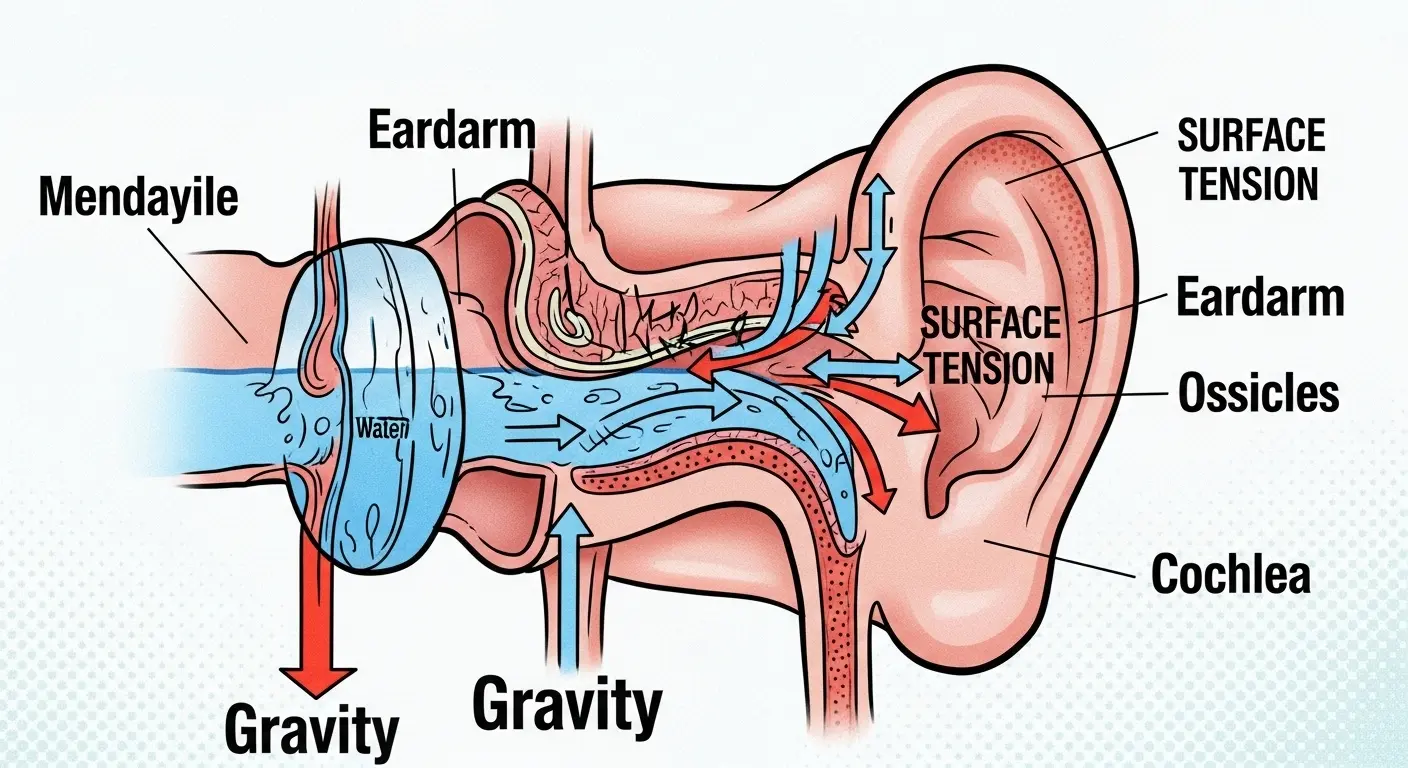
It happens. You, a terrestrial biped, voluntarily submerge yourself in a significant body of H₂O. Upon re-emerging, you find a small, persistent quantity of this liquid has become trapped within your external auditory canal. The result is a sloshing sensation, muffled hearing, and a general sense of asymmetrical imbalance. Most humans find this irritating. I find it a fascinating, small-scale demonstration of fluid dynamics.
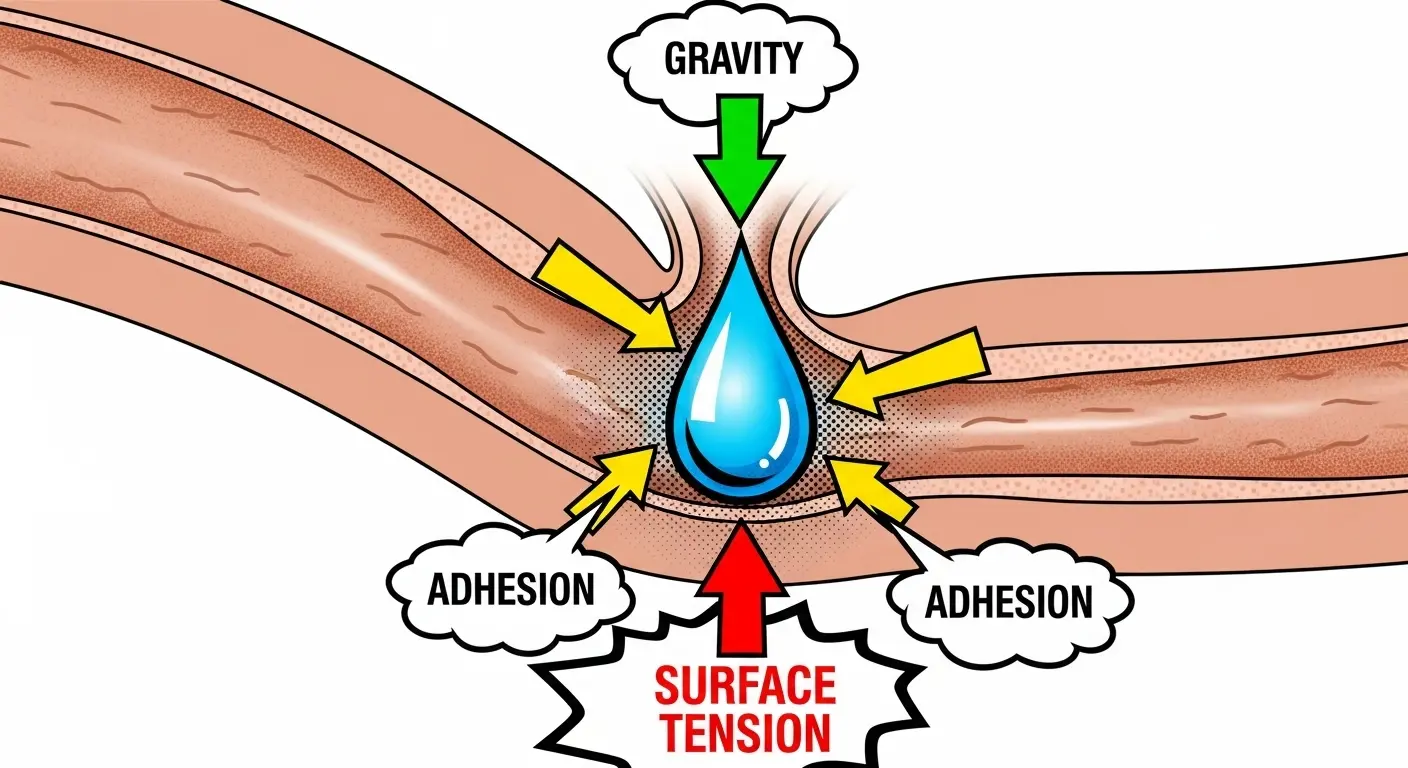
The primary culprit is a force you rarely consider: surface tension. This is the tendency of liquid molecules to cohere, creating a thin, resilient film. In the narrow, complex topography of your ear canal, this film can adhere to the skin, forming a stubborn liquid plug that defies the simple pull of gravity. To defeat this foe, we must not panic; we must apply physics. Here are several methods to resolve your auditory fluid retention issue, analyzed for maximum efficiency.
Method 1: The Gravity and Inertia Maneuver
This is the most intuitive approach, often performed instinctually. It involves leveraging two fundamental forces to overcome the liquid’s adhesive properties.
- Step 1: Tilt your head so the afflicted ear is parallel to the planet’s surface. This aligns the gravitational vector for optimal fluid extraction.
- Step 2: Gently pull on your earlobe. This action slightly straightens the Eustachian tube, reducing topographical obstructions.
- Step 3: Introduce kinetic energy. Jump up and down on one foot. The jarring motion provides the necessary force to break the surface tension seal, allowing gravity to complete the fluid’s egress.
Scientific Principle: You are using gravitational potential energy and inertia to overwhelm the cohesive and adhesive forces of the water molecules. It is brute force on a micro-scale.
Method 2: The Pressure Differential Technique
If gravity alone is insufficient, we can manipulate air pressure. This method, a variation of the Valsalva maneuver, aims to dislodge the water from behind.
- Step 1: Inhale a standard volume of atmospheric gas.
- Step 2: Seal your airway by pinching your nostrils closed and shutting your mouth.
- Step 3: Gently attempt to exhale through your sealed nose. Do NOT exhale with excessive force. The goal is a mild pressure increase, not cranial detonation.
- Step 4: Listen for a subtle ‘pop.’ This indicates a pressure equalization that may have been sufficient to shift the fluid blockage.
Scientific Principle: You are creating a positive pressure system in your nasopharynx that travels up the Eustachian tube, pushing on the trapped water from the inside out.
Method 3: The Fluid Displacement Principle
This appears counterintuitive, like fighting fire with more fire, but the physics are sound. The goal is to break the existing surface tension seal by introducing more liquid.
- Step 1: Lie on your side, with the unaffected ear on the pillow.
- Step 2: Using a clean dropper, introduce a few drops of lukewarm water or a sterile saline solution into the affected ear canal.
- Step 3: Wait approximately 5-10 seconds. The new water will merge with the trapped water, increasing its mass and volume.
- Step 4: Quickly turn your head over, allowing the now-larger, heavier body of water to drain out.
Scientific Principle: By adding more fluid, you create a single, larger mass of water. The increased weight and volume are often enough to break the delicate surface tension that held the smaller amount in place.
When to Abort the Experiment
While these methods are generally effective for simple cases of trapped water, certain variables require consulting a qualified biological technician (i.e., a doctor). If you experience significant pain, discharge, dizziness, or hearing loss, cease all home-based experimentation immediately. Your system may have a more complex issue, such as an infection or impacted cerumen (earwax), that requires professional intervention. The universe is complex, and sometimes a simple fluid dynamics problem is a symptom of something more.